GENERIC NAME: Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids
BRAND NAME(s): Mercola Krill Oil, Red Whale Krill Oil, Schiff MegaRed Omega-3 Krill Oil, Neptune Krill Oil.
OTHER NAME(s): Aceite de Krill, Antarctic Krill Oil, Acides Gras Oméga 3, Acides Gras N-3, Acide Docosahexaénoïque, Acides Gras Polyinsaturés, Acides Gras W3, Concentré de Protéines Marines, DHA, Docosahexanoic Acid, Euphausiacé, Euphausiids Oil, Huile d’ Euphausia Superba, EPA, Euphausia Superba Oil, Huile de Krill, Huile de Krill Antarctique, Huile d’Oméga 3, Omega 3, Omega-3 Fatty Acids, Omega-3, Marine Protein Concentrate, n-3 Fatty Acids, Oméga 3, Omega-3 Fatty Acids, Omega-3 Oil, W-3 Fatty Acids, Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids.
WHAT IS KRILL OIL?
Krill oil is an oil derived from krill, shrimp—like crustaceans. Krill (Euphausia superba) are found in the colder waters of the ocean. Primarily, they serve as a food source for other animals found in the ocean such as whales, penguins, seals, squid and fish. Two of the most important components present in the krill oil are omega-3 fatty acids similar to fish oil, mainly eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA).
Omega-3 are the fatty acids, a type of unsaturated fatty acid, that play an important role in brain and nerve functioning. Omega-3 fatty acids are also known as “essential fatty acid”. Its because human body can’t produce them and they can be obtained only from food.
There are three main types of omega-3 fatty acids —
- Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA)
- Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA)
- Alpha-linolenic acid (ALA)
Krill oil is used for heart ailments, dry eye disease, high levels of cholesterol in the blood (hyperlipidemia) and high levels of fats called triglycerides in the blood (hypertriglyceridemia). (SEE ALSO: Omega-3 Foods : 10 Best Source of Omega-3 Fatty Acids)
This oil has also been used to treat high blood pressure (hypertension), stroke, cancer, osteoarthritis, depression and premenstrual syndrome (PMS). However, more research are needed to support these benefits. Here, patients are advised to speak with their doctor or health care provider prior to using krill oil for any condition.
HOW DOES IT WORK?
Krill oil is rich in fatty acids similar to that of the fish oil. These fats are believed to reduce cholesterol, decrease swelling and make blood platelets less sticky and help to reduce the chance of forming blood clots.
Do not take krill oil in larger amounts or for longer than recommended.
DRUG INTERACTIONS:
Moderate Interaction:
Anticoagulant or Antiplatelet drugs that slow blood clotting may interact with krill oil. These medications along with krill oil may increase the chance of easy bruising and bleeding. Some drugs that slow blood clotting include —
- Warfarin
- Aspirin
- Clopidogrel (Plavix)
- Diclofenac (Voltaren, Cataflam)
- Heparin
- Ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin)
- Naproxen (Anaprox, Naprosyn)
- Dalteparin (Fragmin)
- Enoxaparin (Lovenox)
Minor Interaction:
Orlistat (Xenical, Alli) used for weight loss may also interact with this oil. (SEE ALSO: Jojoba Oil Benefits for Skin and Hair)
WHAT ARE THE SIDE EFFECTS OF KRILL OIL?
Seek emergency medical support if you’ve any of these symptoms of an allergic reaction— difficulty breathing, swelling of the face, hives, lips, tongue, or throat. Stop using krill oil and call your doctor if you have any of these serious side effects —
- Chest pain
- Fever
- Flu symptoms
- Chills
- Body aches
- Uneven heartbeats
Moderate side effects of krill oil may include —
- Mild skin rashes
- Back pain
- Fishy aftertaste
PRECAUTIONS:
Do not use krill oil if you are allergic to shrimp, fish or any other type of seafood. Ask your doctor before using this oil if you have —
- Liver disease
- Diabetes
- A pancreas disorder
- Blood clotting disorder
- Underactive thyroid
- If you consume excessive amount of alcohol
KRILL OIL VS FISH OIL:
What is The Difference Between Krill Oil and Fish Oil?
Fish oil is obtained from the tissues of cold—water oily fishes, such as salmon, mackerel, herring, sardines and anchovies. Whereas, krill oil is derived from the Antarctic krill (Euphausia superba), a small shrimp—like crustacean. (SEE ALSO: Importance of Omega-3 Fatty Acids : You Must Know)
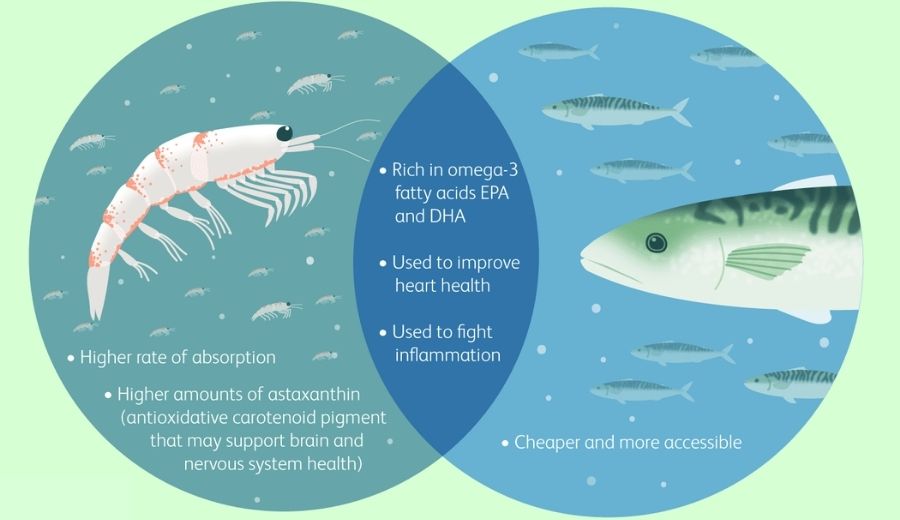
Krill oil and fish oil both are a good source of omega-3 fatty acids, mainly eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA). Particularly, krill oil contains rich amounts of choline-containing phospholipids and a phosphatidylcholine of 34 grams per 100 grams serving. Krill oil also contains a good amount of astaxanthin (a carotenoid pigment) at 0.1 to 1.5 mg per milliliter depending on the processing methods. Astaxanthin is responsible to give krill its red color.
Which One is Better — Krill Oil or Fish Oil?
Now the question may arise — in krill and fish oil which one is better for you? Let’s know —
Krill oil is usually more stable than that of the fish oil. Krill oil contains comparatively better taste and reduced fishy smell which make it better than fish oil. In addition to this, krill oil can be better absorbed than fish oil. However, more scientific studies are needed to prove this.
Krill oil contains more antioxidants than fish oil. Krill oil is rich in an antioxidant known as astaxanthin, which is not found in most fish oils.
An another advantage of krill oil over fish oil is that it can improve heart health, possibly to a greater extent.
REFERENCES:
- Drugs.com. Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids; drugs.com; Accessed Jan. 21, 2013.
- Incorporation of EPA and DHA into plasma phospholipids in response to different omega-3 fatty acid formulations–a comparative bioavailability study of fish oil vs. krill oil; Authors: Jan Philipp Schuchardt, Juliane Neubronner, Inga Schneider, Henrike Meyer, Clemens von Schacky and Andreas Hahn; PMID: 21854650. PMCID: PMC3168413. DOI: 10.1186/1476-511X-10-145.
- Metabolic effects of krill oil are essentially similar to those of fish oil but at lower dose of EPA and DHA, in healthy volunteers; Authors: Stine M Ulven, Bente Kirkhus, Samar Basu, Elisabeth Elind, Amandine Lamglait, Trond Haider, Kjetil Berge, Hogne Vik and Jan I Pedersen; PMID: 21042875. PMCID: PMC3024511. DOI: 10.1007/s11745-010-3490-4.
- Krill Oil vs Fish Oil – What’s the difference between them?; Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Apr 12, 2019.
