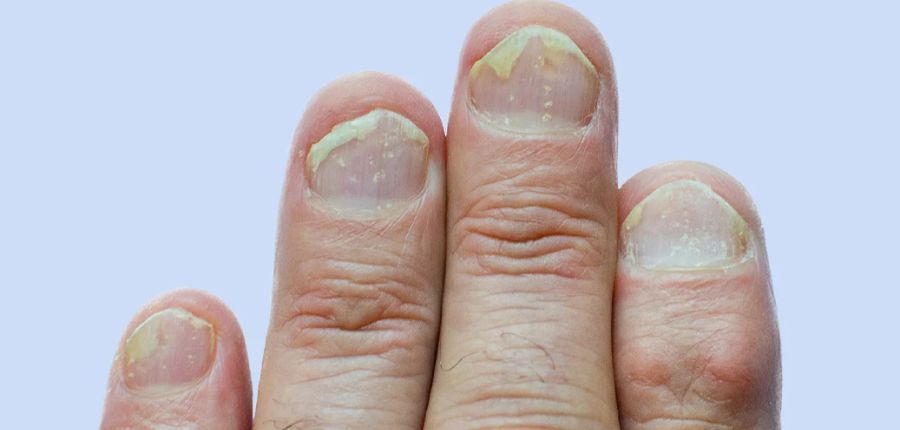
Nail psoriasis is a chronic skin condition that affects the nails, causing a range of symptoms that can be both uncomfortable and visually distressing. Often confused with nail fungus due to their similar appearance, nail psoriasis is a distinct condition with its own set of causes, symptoms, and treatment options.
In this article, we will explore nail psoriasis in depth, including images to help distinguish it from nail fungus, its causes, symptoms, prevention strategies, and available treatments, including medications.
Nail Psoriasis vs. Nail Fungus
Before delving into nail psoriasis, it’s essential to differentiate it from nail fungus. Both conditions can affect the nails, but they have distinct characteristics. (1) (5)
Nail Psoriasis:
- Nail psoriasis is an autoimmune condition where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks healthy nail tissue;
- It can affect both fingernails and toenails;
- Common symptoms include pitting (small dents or depressions in the nail surface), ridges, thickening, discoloration (typically yellow-brown), and nail detachment (onycholysis);
- Pain and discomfort may accompany nail psoriasis, especially when the nails become severely affected; and
- Nail psoriasis is not contagious and is linked to underlying autoimmune factors.
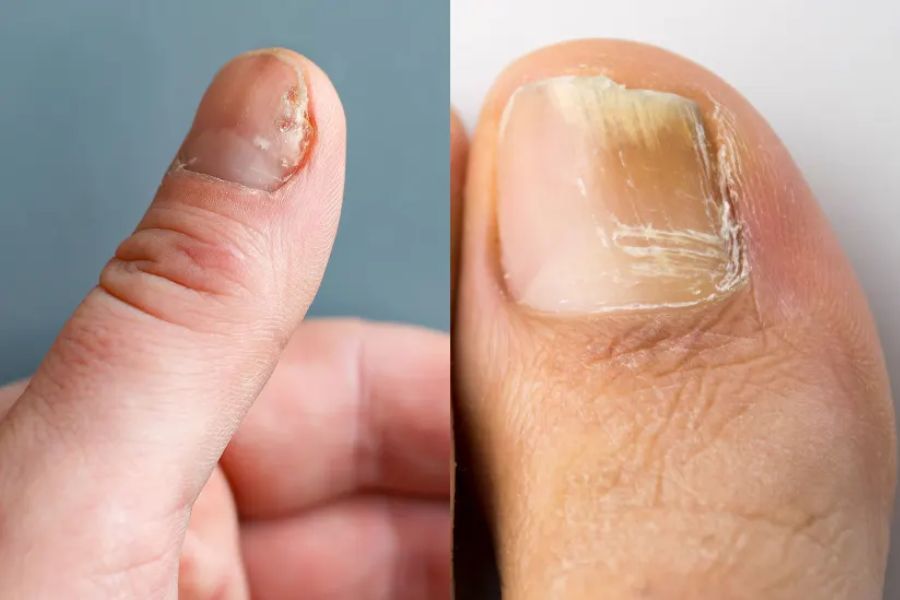
Nail Fungus (Onychomycosis):
- Nail fungus is a fungal infection that typically begins as a small white or yellow spot under the nail;
- It often affects toenails but can also impact fingernails;
- Symptoms may include thickening, discoloration (usually yellow or white), brittleness, and nail debris;
- Nail fungus can spread easily, and it’s contagious; and
- Fungal infections are caused by various fungi and are not linked to autoimmune factors.
Causes Of Nail Psoriasis
The exact cause of nail psoriasis is not fully understood, but it is believed to involve genetic and autoimmune factors.
People with a family history of psoriasis are more likely to develop nail psoriasis. Certain triggers can exacerbate the condition, such as stress, injury to the nails, or infections.
Symptoms Of Nail Psoriasis
Nail psoriasis can present a range of symptoms that may vary in severity. Common signs of nail psoriasis include: (1)
- Pitting: Small pits or dents on the nail surface;
- Ridges: Horizontal or vertical ridges on the nails;
- Thickening: Nails may become thicker and harder;
- Discoloration: Nails may turn yellow, brown, or have white spots;
- Onycholysis: Separation of the nail from the nail bed;
- Crumbling: Nails may become brittle and prone to breaking; and
- Pain: Severe cases can lead to discomfort and pain.
It’s important to note that nail psoriasis can coexist with psoriasis affecting the skin or joints.
Prevention Strategies
While nail psoriasis cannot always be prevented, there are strategies to manage and reduce its impact:
- Maintain Good Nail Hygiene: Keep nails clean and dry to minimize the risk of infection;
- Avoid Trauma: Protect your nails from injury, and avoid biting or picking at them;
- Manage Stress: Stress can exacerbate psoriasis symptoms, so practicing stress-reduction techniques can be helpful;
- Moisturize: Apply a moisturizer to the nails and cuticles regularly to prevent drying; and
- Seek Treatment Early: If you suspect nail psoriasis, consult a dermatologist promptly to begin treatment and prevent further damage.
Treatment Options For Nail Psoriasis
Treatment for nail psoriasis aims to improve the appearance of the nails, reduce discomfort, and slow down disease progression. Options include: (2)
- Topical Treatments: These include corticosteroid creams, calcineurin inhibitors, and vitamin D analogs. They are applied directly to the nails.
- Oral Medications: In severe cases, oral medications like methotrexate, acitretin, or biologics may be prescribed to suppress the immune response.
- Light Therapy (Phototherapy): Exposure to UVB light can help improve nail psoriasis symptoms.
- Nail Injections: Corticosteroids or biologics can be injected directly into the affected nails.
- Nail Care: Regular trimming, filing, and moisturizing can help manage symptoms.
In some cases, a combination of these treatments may be recommended, depending on the severity of the condition.
Medication For Nail Psoriasis
Certainly, medication is an essential component of the treatment plan for nail psoriasis. The choice of medication depends on the severity of the condition and how it responds to different treatments. Here are some common medications used to manage nail psoriasis: (2) (3) (4)
- Topical Corticosteroids: These are creams, ointments, or solutions applied directly to the affected nails. Corticosteroids help reduce inflammation and can improve the appearance of the nails. However, they may not work well for severe cases.
- Calcineurin Inhibitors: Medications like tacrolimus and pimecrolimus can be applied topically to manage nail psoriasis. They work by suppressing the immune response in the nails, which reduces inflammation and symptoms.
- Vitamin D Analogues: Calcipotriene is a topical vitamin D analog that can be used to treat nail psoriasis. It helps regulate skin cell growth and can be effective in improving nail symptoms.
- Oral Medications: For more severe cases of nail psoriasis or when it is associated with widespread psoriasis on the skin or joints, oral medications may be prescribed. These can include:
- Methotrexate: An immunosuppressive drug that can slow down the growth of skin cells and reduce inflammation.
- Acitretin: A retinoid medication that can help control psoriasis symptoms.
- Biologics: These are newer medications that target specific immune system components involved in psoriasis. They are usually reserved for severe cases and are administered by injection or infusion.
- Nail Injections: In some instances, healthcare providers may recommend injecting corticosteroids or biologics directly into the affected nails to target the inflammation locally.
- Phototherapy (Light Therapy): Phototherapy, specifically using UVB light, can be effective in treating nail psoriasis. This treatment is typically administered by a dermatologist.
It’s important to note that the choice of medication and treatment approach should be determined by a healthcare professional based on the individual’s specific condition and needs. Nail psoriasis can be a chronic condition, and management often requires ongoing treatment and monitoring to achieve the best results. Regular follow-ups with a dermatologist are crucial to assess the effectiveness of the chosen treatment and make any necessary adjustments.
Take Away
Nail psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune condition that affects the nails, causing various symptoms that can impact both appearance and comfort. It is important to differentiate nail psoriasis from nail fungus, as the treatment approaches are different.
While there is no cure for nail psoriasis, early intervention and appropriate treatment can effectively manage the condition, improve nail health, and enhance overall quality of life. If you suspect you have nail psoriasis, consult a dermatologist for a proper diagnosis and personalized treatment plan.