Your brain has several different parts that perform different functions, each of which has its own areas and characteristics. One of the main parts of your brain is called the cerebral cortex, and it plays an important role in your thinking, memories, emotions, language and decision-making processes. Here’s what you need to know about the cerebral cortex and how it relates to your mind and body.
What is cerebral cortex?
The cerebral cortex is the outermost layer of the brain and is responsible for higher-level cognitive functions such as language, memory, and planning. It is also involved in processing sensory information from the body.
The cortex is divided into four main lobes: the frontal lobe, parietal lobe, temporal lobe, and occipital lobe. Each lobe has specific functions.
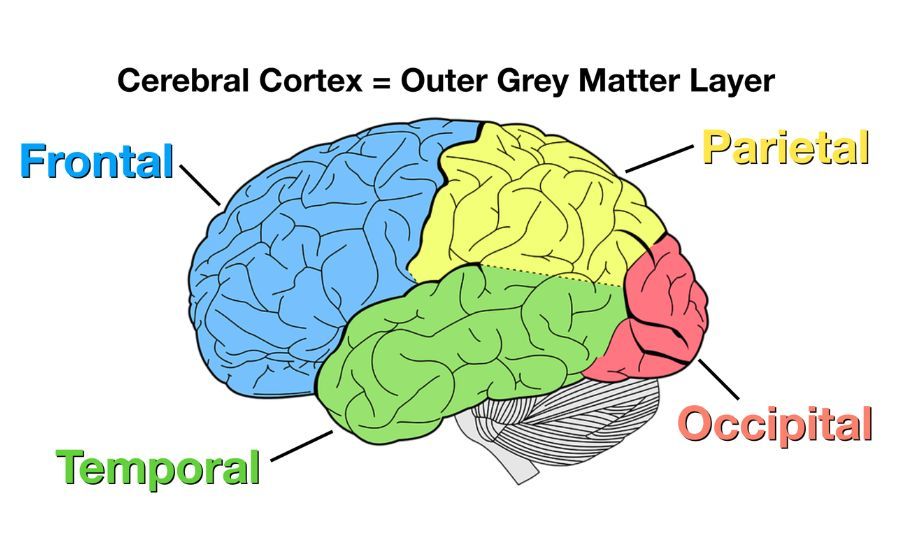
For example, the frontal lobe is responsible for executive function, while the temporal lobe processes auditory information. Together with the hypothalamus, these parts form the limbic system.
In this sense, limbic refers to structures located along both sides of the brain stem that are important for emotion. They include the amygdala, hippocampus, thalamus, and cingulate gyrus.
The amygdala plays a key role in emotions related to fear or anger by sending signals to the rest of the brain; the hippocampus is crucial for long-term memory by taking information from short-term memory and storing it for future use; and the thalamus helps relay messages between different regions of the brain before deciding where they should go next.
What does cerebral cortex do?
The cerebral cortex is the outermost layer of the brain and is responsible for higher cognitive functions such as decision-making, problem-solving, and processing emotions. It is also responsible for our sense of self-awareness and consciousness.
The cortex is divided into four main lobes: the frontal lobe, parietal lobe, temporal lobe, and occipital lobe. Each of these lobes is responsible for different functions. For example, the frontal lobe is involved in movement and voluntary actions.
The temporal lobe is involved in hearing and language comprehension. The occipital lobe helps process visual information from your eyes.
Finally, the parietal lobe processes sensory information from other parts of your body. Damage to this area can result in neurological problems that affect sensation, like pain or pressure.
The frontal lobe controls personality, social behaviors, and decision-making. Damage to this area can lead to changes in behavior or personality changes that can be more pronounced with age because we rely on it less as we get older.
The temporal lobe enables you to understand speech sounds and words through hearing, even if you’re not looking at the person speaking.
The 2 hemispheres of the brain and their functions:
The cerebral cortex is divided into two hemispheres, the left and right. Each hemisphere controls the opposite side of the body. The hemispheres are further divided into four lobes- the frontal, parietal, temporal, and occipital.
The frontal lobe contains areas for speech production, motor control, and emotions. Damage to this area can result in problems with speaking or understanding language as well as changes in mood or personality.
The parietal lobe contains areas for sensory information processing such as hearing and touch. Damage here can lead to difficulties with sensory perceptions such as pain or temperature.
The temporal lobe contains parts of the brain important for memory and emotional responses. Damage to this area can cause memory loss, difficulty concentrating, depression, or anxiety.
The occipital lobe processes visual information from the eyes and helps produce what we see. Damage here may lead to partial blindness or color blindness.
The 4 lobes in detail:
The cerebral cortex is divided into four lobes: the frontal lobe, temporal lobe, parietal lobe, and occipital lobe. Each of these lobes is responsible for different functions.
The frontal lobe helps control movement, problem solving, memory, language and other complex skills; it also houses a region called Broca’s area which has been linked to speech production. The temporal lobe deals with long-term memory storage and processing; this is where memories are consolidated from short-term memories in the hippocampus.
Additionally, the amygdala (which can be thought of as part of this lobe) handles emotional memories including fear conditioning. Finally, the occipital lobe processes visual information. It does not just receive sensory input, but also sends out nerve impulses about what it sees.
The primary visual cortex receives most of the input from the eye muscles and retinae (the photosensitive layer at the back of the eye). Other areas process color signals and shape recognition.
In order to understand how all these parts work together, try closing your eyes without moving your head or neck so that you are looking straight ahead with your eyelids shut tight.
Taking care of your cerebral cortex:
Just as you take care of your heart and lungs, it’s important to take care of your brain. The cerebral cortex is responsible for many functions, including memory, attention, language, and consciousness.
Here are a few tips for keeping your cortex healthy
- Eat lots of leafy greens, berries, and fish (all rich in omega-3s).
- Practice mindfulness meditation.
- Get plenty of sleep.
- Exercise regularly
- Eat less sugar. The brain uses up a lot of glucose, and too much sugar can leave you feeling foggy.
- It’s also important to eat a balanced diet because vitamins play an important role in helping your body function properly.
- Your brain relies on proper circulation, so make sure to exercise and get enough fluids. If you’re experiencing symptoms such as severe headaches or changes in mood, don’t hesitate to visit your doctor.
Conclusion
The cerebral cortex is responsible for a lot of what makes us human. It’s involved in everything from processing sensory information to planning and executing complex movements.
